Last updated on September 22nd, 2016 at 12:06 am
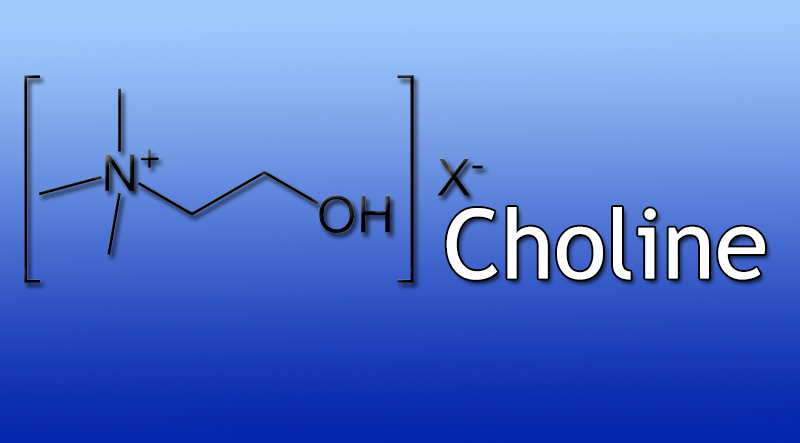
Choline is an essential nutrient that is necessary for healthy cell membranes and the production of phosphatidylcholine. It also aids in the transport of lipids, or fats, from the liver.
- Reduces fatigue
- Helps prevent insomnia
- Aids in kidney function
- Faciliates memory function and muscular control
- Helps prevent headaches
- Reduces Brain fog
It is also the precursor to acetylcholine, one of the many neurotransmitters involved in memory. Most people tend to get enough of it from diet alone, however, some nootropic users feel the need to supplement it when taking racetam drugs. This is because the racetam drugs tend to deplete acetylcholine levels in the brain which causes headache and brain fog in many users. Choline supplementation often remedies these problems.
Table of Contents
Benefits
While over supplementation will not provide any significant benefits, those who are deficient, however, will notice significant improvements in their quality of life. Mild choline deficiency symptoms include:
- Fatigue
- Insomnia
- Poor kidney function
- Poor memory
- Poor muscular control
- Headache
- Brain fog
If you have more than 3 of the above symptoms then supplementation may benefit you.
Side effects of Choline
Choline is a very safe nutrient and will not cause any serious complications taken in the long-term, though, some people are susceptible to a condition called fish odor syndrome. This syndrome is caused by a genetic disorder and is characterized by the inability of the body to metabolize trimethylamine, a compound of which choline is a precursor to, which causes the subject to develop a fishy odor in their sweat, urine and breath after consumption of choline-rich foods.
This syndrome can also occur in healthy people who take too much of it and leave their body unable to metabolize the extra trimethylamine. The symptoms reside after supplementation is ceased.
Over supplementation can also cause:
- Depression
- Lethargy
- Loss of motivation
- Decreased appetite
- Excessive sweating
Side effects usually subside after ceasing supplementation.
Best choline supplements to take
There are many versions of choline on the market and many brands as well, but many experienced nootropic users don’t bother with the lower quality compounds as they tend to have poor bioavailability thereby requiring a higher dosage. Below is a list of the supplements available on the market sorted from lowest quality to highest quality:
- Choline Bitartrate – Lowest Quality
- Choline Citrate
- Soy Lecithin (Phosphatidylcholine)
- Centrophenoxine
- CDP-Choline (Citicoline)
- Alpha-GPC – Highest Quality
Which supplement is of the highest quality is open to debate, however, it is generally accepted that both Alpha-GPC and CDP-Choline are excellent sources. Citicoline also comes with a few benefits of its own:
- Increased energy
- Increased focus
- Increased release of HPA axis hormones (LH, FSH, GH and TSH)
- Improved memory
The benefits of CDP-Choline are mainly mediated by the fact that it increases dopamine and muscarinic receptor density.
Both Alpha-GPC and CDP-Choline are highly bioavailable and thus you only have to take a small amount to attain the benefits when compared to a lower quality source such as Choline Bitartrate.
References
Giménez, R., J. Raïch, and J. Aguilar. “Changes in Brain Striatum Dopamine and Acetylcholine Receptors Induced by Chronic CDP-choline Treatment of Aging Mice.” British Journal of Pharmacology 104 (1991): 575-78. NCBI. Web. <http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1908237/>.